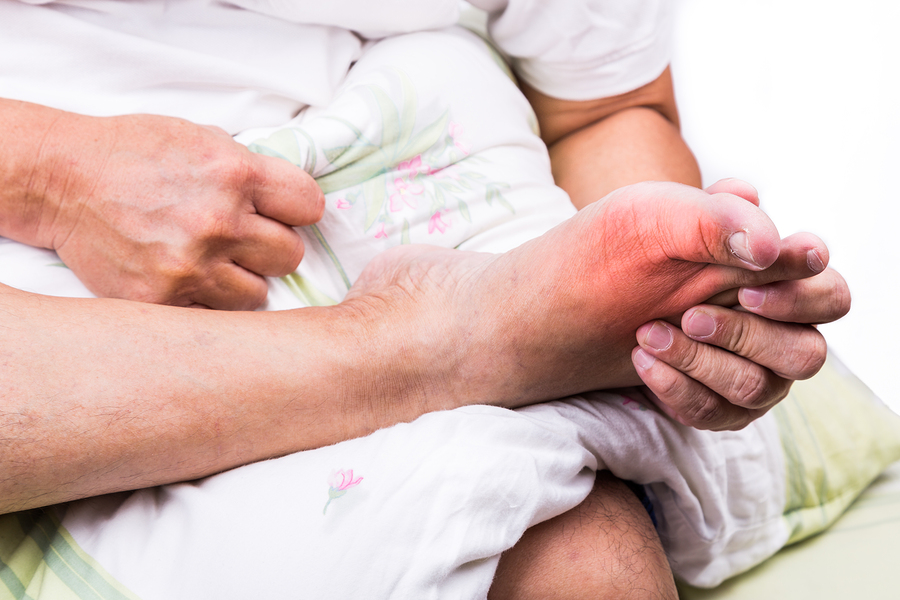
Gout
Gout is the recurrent attacks of joint inflammation caused by deposits of uric acid crystals in the joints, especially in the base of the big toe.
Gout may also involve the elbow, knee, hand, foot, ankle and/or shoulder. It affects adults of both sexes but is 20 times more frequent in men than women.
Frequent Signs and Symptoms include: Sudden onset of severe pain in the inflamed joint, usually at the base of the big toe or larger joints. Involved joints are red, hot, swollen and very tender. Skin over joint is red and shiny. Fever, sometimes.
Causes include: A high level of uric acid in the blood due to increased production of uric acid or decreased elimination of uric acid by the kidneys.
Risk increases with:
- Use of diuretic drugs (water pills) such as furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide
- Use of some antibiotics
- Some blood diseases such as polycythemia and leukemia
- Men over 60
- Family history of gout
- Obesity
- Many disorders including thyroid problems, kidney disease, anemia, hyperlipidemia, high blood pressure, diabetes and vascular disease.
- Trauma, surgery, and radiation treatment
- Eating large amounts of anchovies, sardines, sweetbreads, kidney or liver
- Chemotherapy may raise uric acid levels
Preventive Measures:
Avoid and/or lessen risk factors when and where possible.
Outcomes:
- The first attack of Gout may last a few days.
- Recurrent attacks are common without treatment to reduce the uric acid level in the blood.
- Symptoms can be eliminated with treatment.
Possible Complications. If untreated, Gout may cause:
- Inflammation of bones, ligaments and tendons.
- Crippled deformed joints.
- Kidney stones.